Acaulospora delicata
(reference accession AZ661)
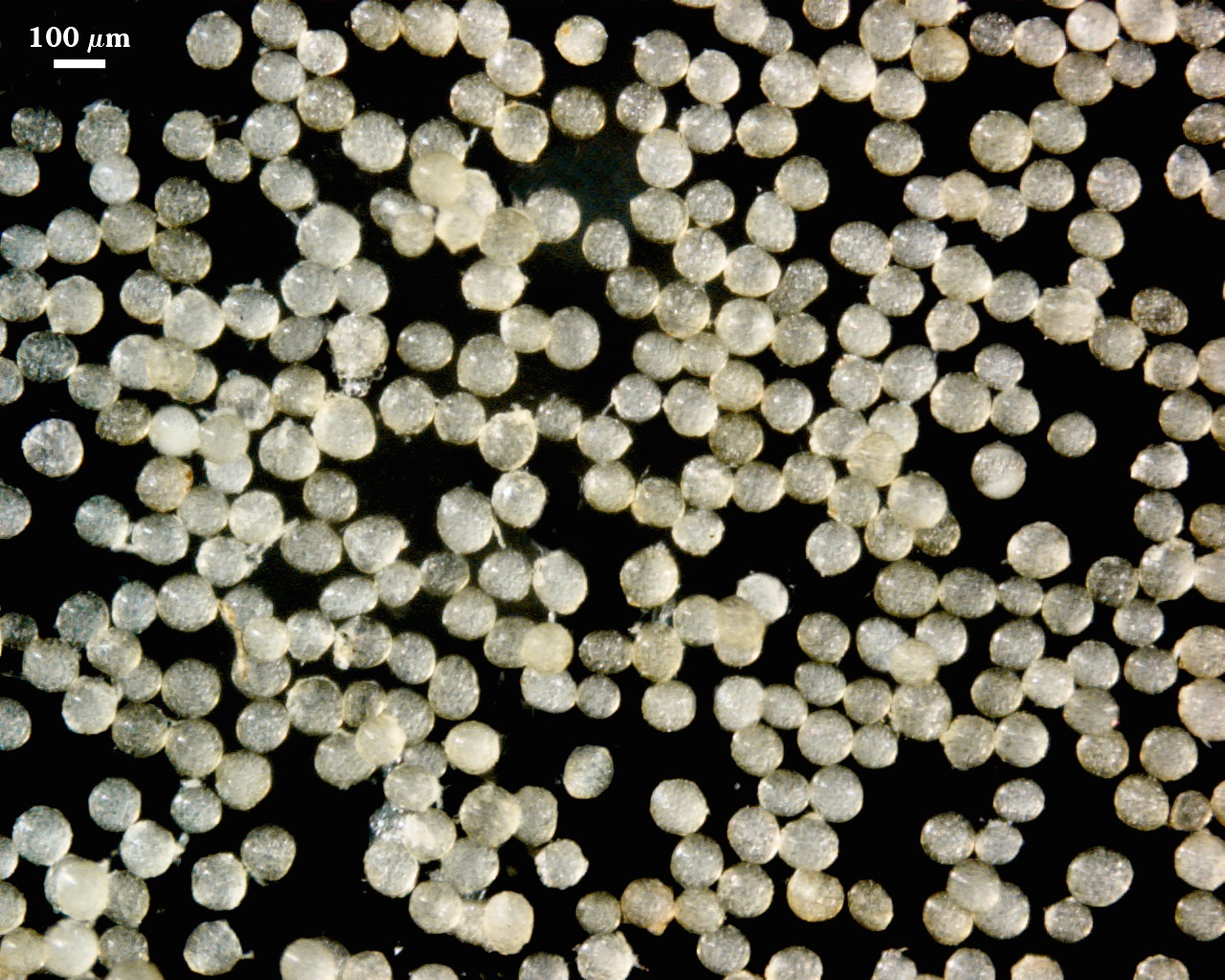
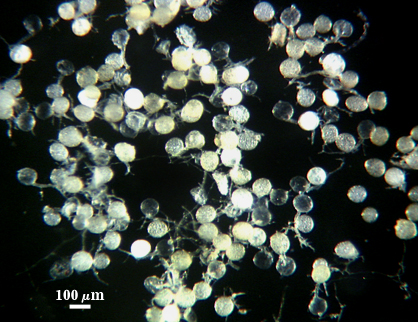
Whole Spores
| Spore Growth | |
|---|---|
 |  |
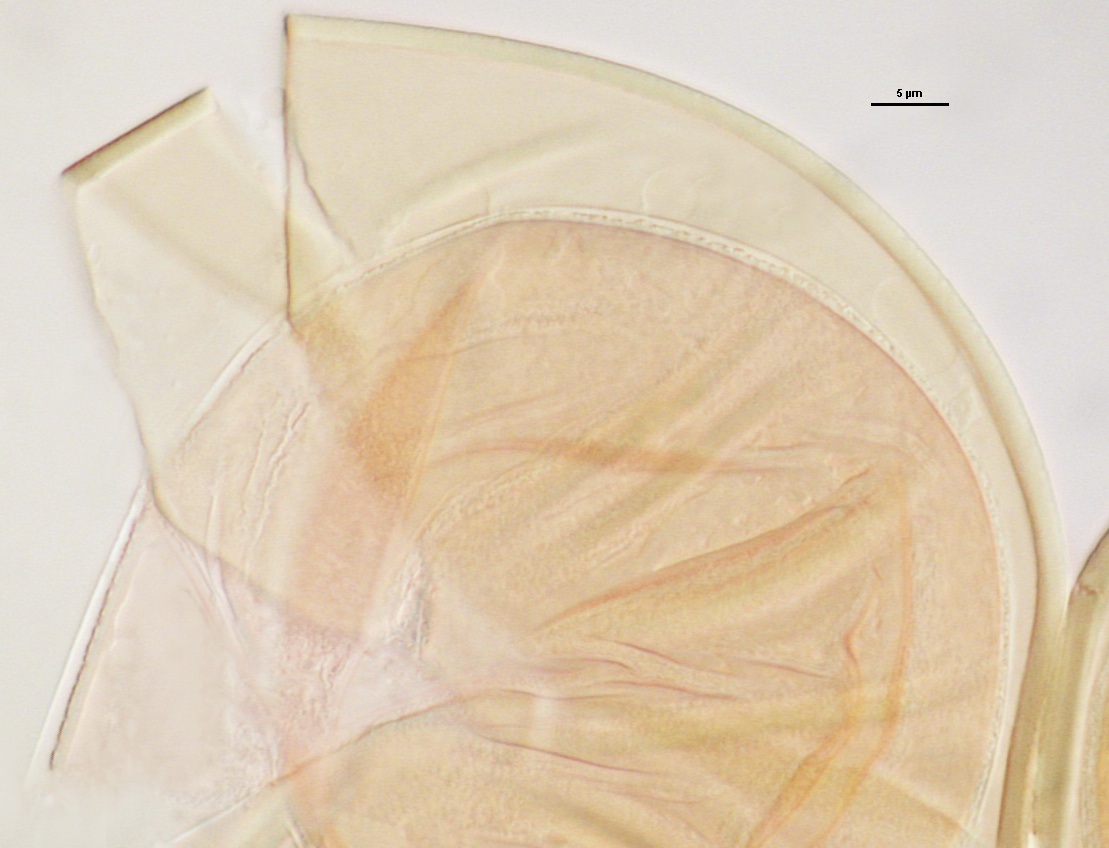
 COLOR: Subhyaline (0/5/10/0) to pale yellow with green tint (0/5/20/0). Most spores extracted from active pot cultures are a very pale yellow.
COLOR: Subhyaline (0/5/10/0) to pale yellow with green tint (0/5/20/0). Most spores extracted from active pot cultures are a very pale yellow.
SHAPE: Mostly globose, subglobose.
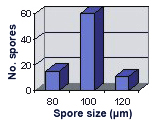
SIZE DISTRIBUTION: 80-120 µm, mean = 99 µm (n=86).
Subcellular Structure of Spores
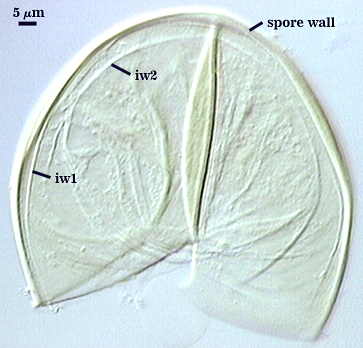
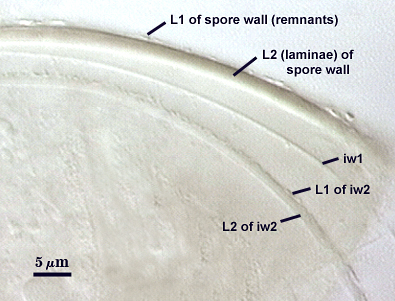
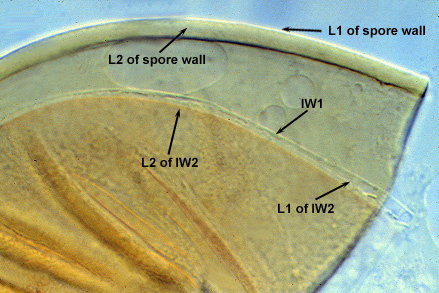
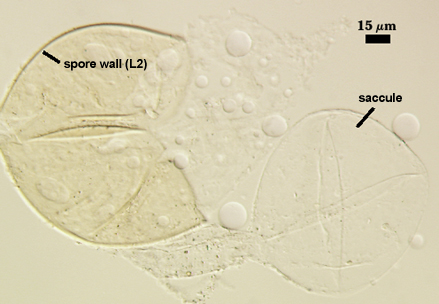
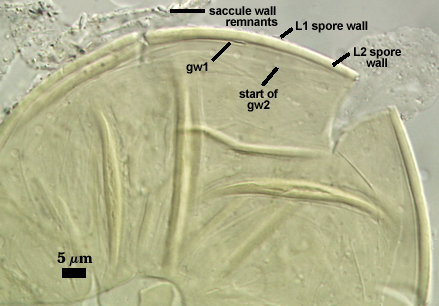
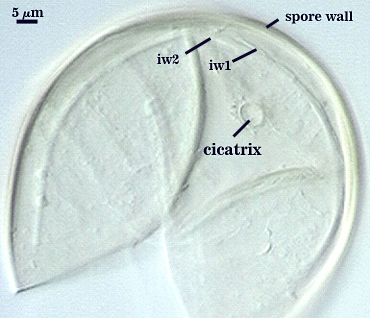
SPORE WALL: Two layers (L1 and L2), the outer layer continuous with the wall of the neck of the parent sporiferous saccule and the inner layer synthesized locally with onset of spore formation.
| Spores mounted in PVLG | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Spores in PVLG & Melzer’s reagent | |
|---|---|
|
|
L1: Hyaline, 0.4-0.8 µm thick when intact, degrading to form a granular coating or sloughing completely.
L2: A layer consisting of very fine and adherent sublayers (or laminae) that often are difficult to discern; very pale yellow (0-0-10-0) in color, and 1.8-3.2 µm thick (mean of 2.4 µm). At maturity, the spore detaches form the saccule and is sessile. It is essentially an ‘endospore’ in that it separates completely from the parent saccule neck and the spore wall has no break or opening in the region of attachment to the saccule neck.
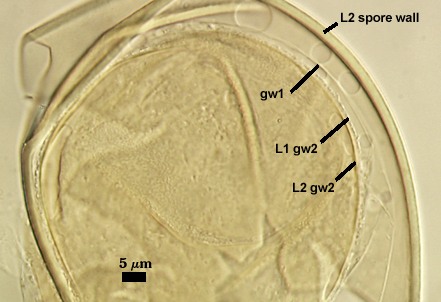
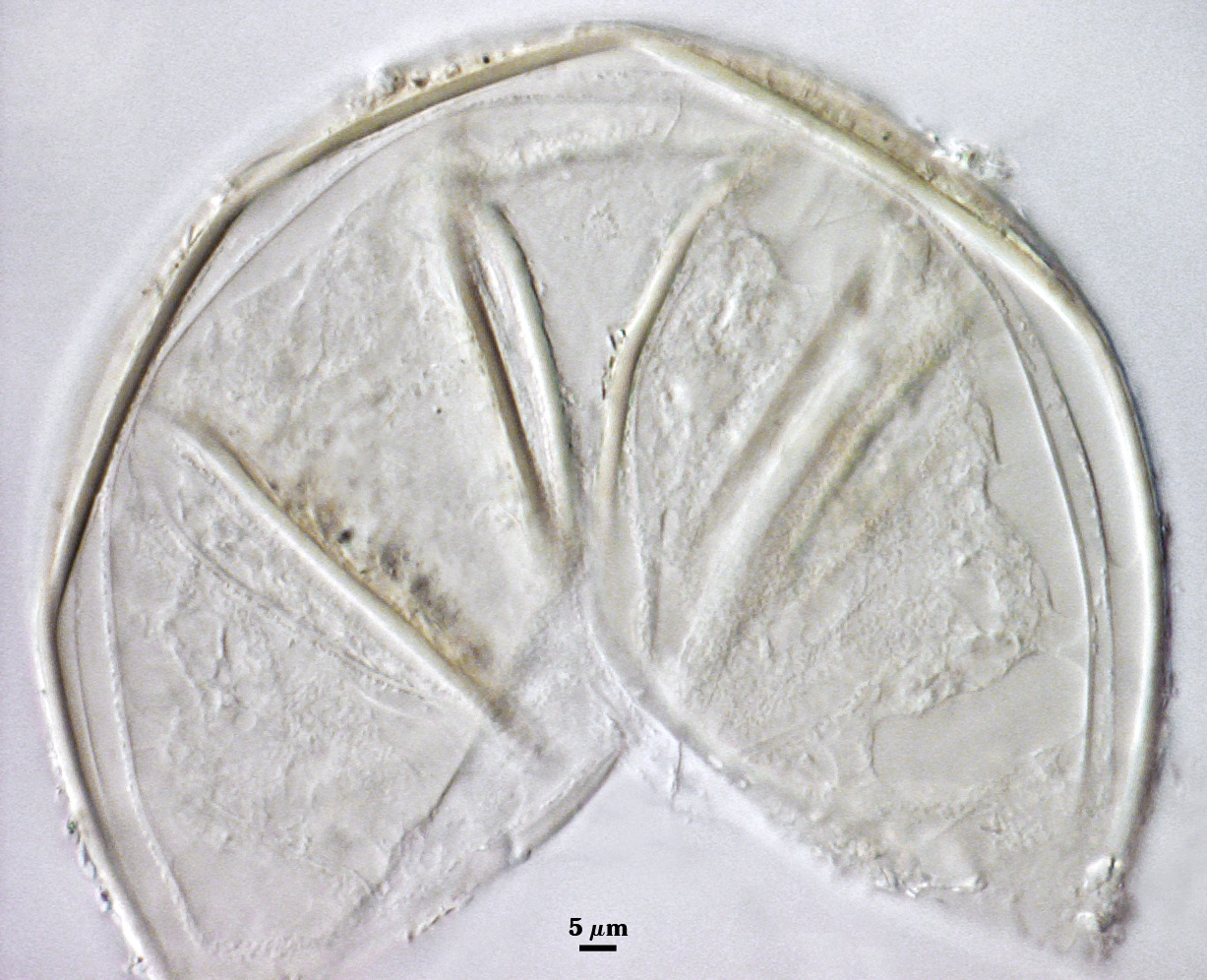
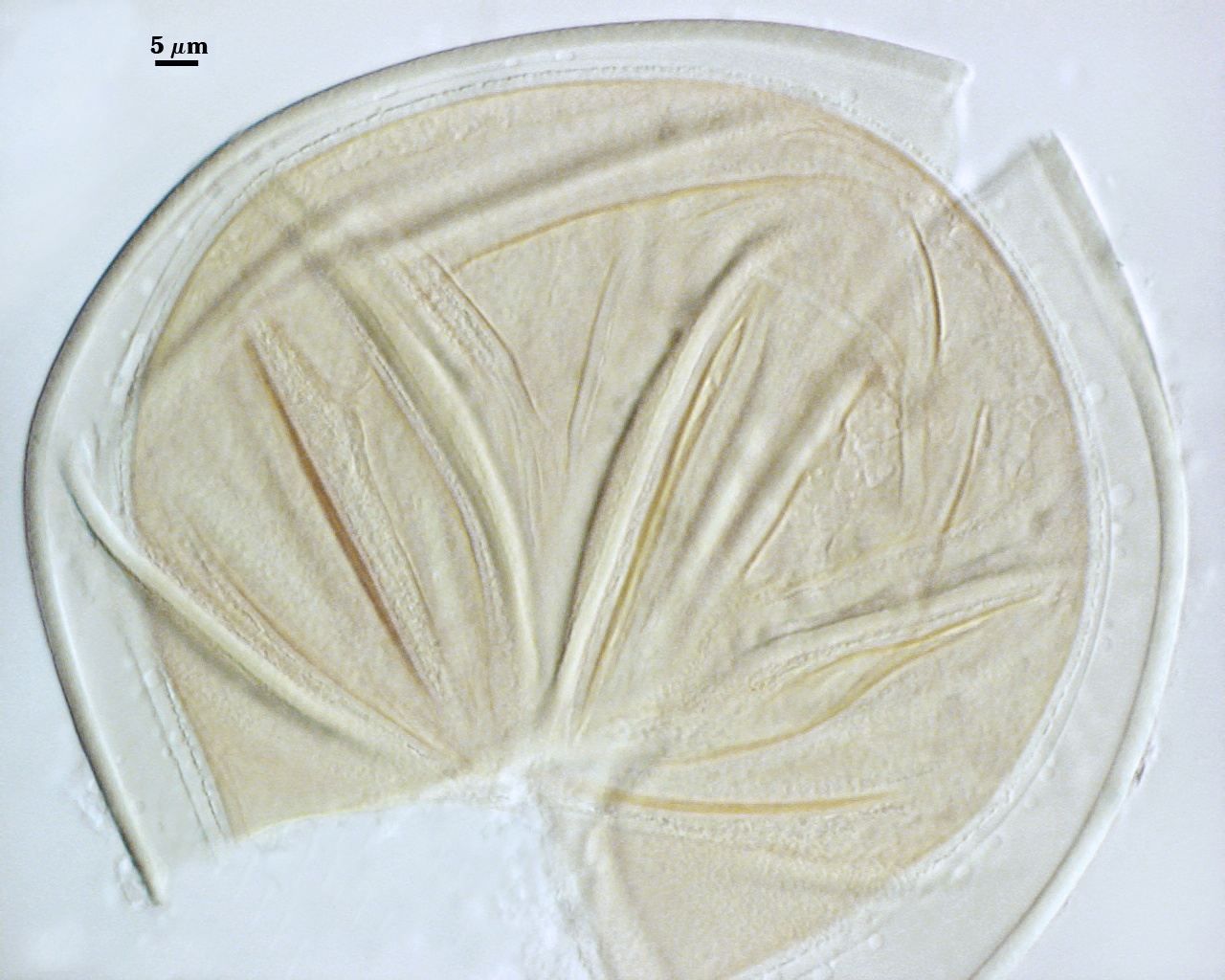
GERMINAL WALLS: Two hyaline flexible inner walls (gw1 and gw2) are formed sequentially in spores after the spore wall has completed differentiation and the spore has ceased expansion.
| Sequence from left to right | |
|---|---|
|
|
GW1: May be bi-layered as is the case for other Acaulospora species, but only one layer is visible, 0.5-0.8 µm thick.
GW2: Consisting of two layers (L1 and L2) that are tightly adherent. The surface of L1 is uniformly covered with granular excrescences (or “beads”) that tend to dislodge with applied pressure or become invisible after the specimen is mounted in PVLG for several months or longer; 0.6-0.8 µm thick when freshly mounted. L2 is 0.6-1.9 µm thick; usually stains light pink (0-5-0-0) to a slightly darker pink (0-10-20-0) in Melzer’s reagent, occasionally showing no reaction.
Cicatrix
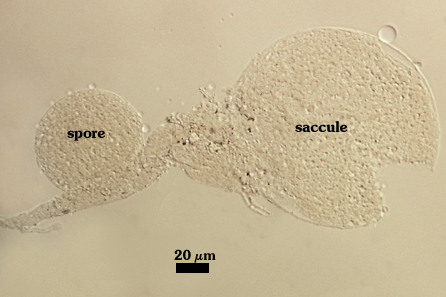
This scar is a remnant of the connection between the spore wall and the wall of the parent hypha (forming the sporiferous saccule) during spore synthesis; diameter is 6.5-9.6 µm (mean = 7.8 µm).
Sporiferous Saccule
COLOR: Hyaline.
SHAPE: Mostly globose
SIZE: 70-80 µm, mean = 78.2 µm.
SACCULE WALL: One layer, smooth surface, 0.6-1.4 µm thick.
DISTANCE FROM SACCULE TO SPORE: 60-100 µm.
Mycorrhizae
Arbuscules and intraradical hyphae stain with considerable variation in intensity with trypan blue, although vesicles and hyphae generally stain darkest. Infection units appear to be patchily distributed with oblong to irregular vesicles often forming in small clusters. Hyphae forming coils are up to 7 µm in width; hyphae growing parallel to the root axis range from 2-4 µm wide.
| Arbuscules in corn roots | |
|---|---|
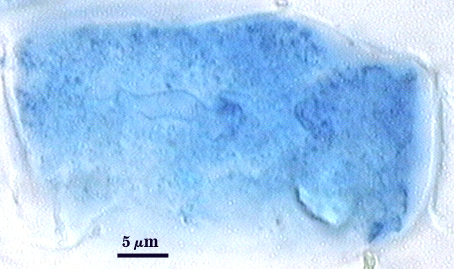 | 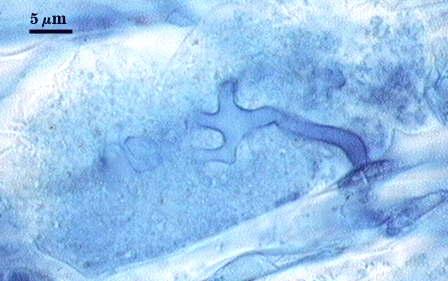 |
| All mycorrhizal structures in corn | ||
|---|---|---|
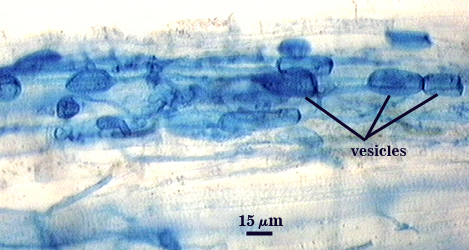 | 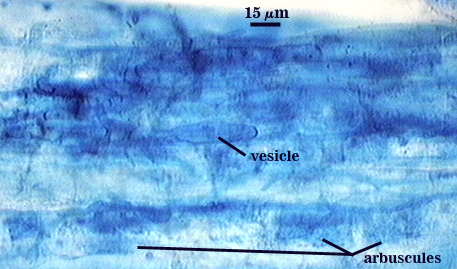 | 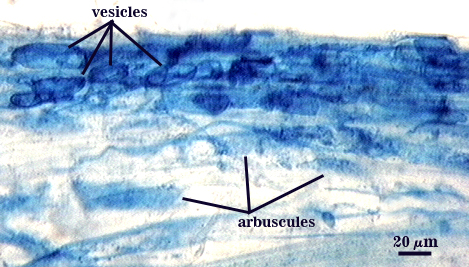 |
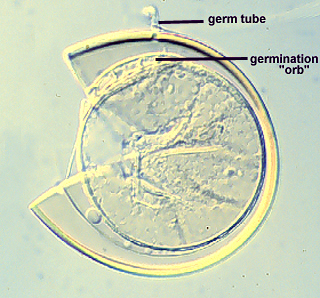
Germination
From hyaline, fragile (too much so to define boundaries in the spore examined) pregermination orb that forms on the surface of the innermost germinal wall (gw2).
Notes
This species is one of only a few in which the inner layer (L2) of the innermost germinal (gw2) wall stains light pink or not at all in Melzer’s reagent. Dark red-brown to dark red-purple are common reactions in most other Acaulospora species.
Links to Gene Sequences in Genbank
Reference
- Walker, C., C. M. Pfeiffer, and H. E. Bloss. 1986. Acaulospora delicata sp. nov. —an endomycorrhizal fungus from Arizona. Mycotaxon 25:621-628.