Analysis of Glomalin
Glomalin is a Glycoprotein
Glomalin is a glycoprotein produced abundantly on hyphae and spores of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soil and in roots. Shortly after Sara Wright and I collaborated on development of a monoclonal antibody specific for Paraglomus occultum, we attempted to produce monoclonal antibodies against other AM fungi. With more recent species (e.g. Rhizophagus intraradices), antibody cell lines were broader in specificity but restricted to Glomeromycota. Using these cell lines, Sara Wright and co-workers discovered they reacted specifically against glomalin. These antibodies then became a tool to detect and quantify glomalin associated with fungal biomass and in a wide range of soils.
| Hyphae and Spores of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal | ||
|---|---|---|
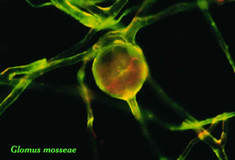 | 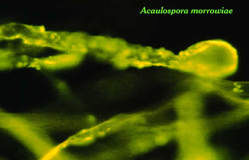 |  |
Glomalin Extraction
Different fractions of glomalin can be extracted using different methods. Glomalin Extraction (.pdf) explains these methods. A sodium pyrophosphate extraction is the harshest and recovers the most soluble pool (easily extractable) as well as the total protein pool (total glomalin). Each of these latter pools can be extracted using different concentrations of sodium citrate and varying the length of autoclaving.
Author:Joe Morton