Diversispora trimurales
Voucher Specimens
This description is a combination of information obtained from the protologue (Koske and Halvorson, 1989), type specimens, and universal patterns of morphological organization and structure in Glomeraceae.
| In PVLG | In PVLG & Melzer’s reagent | |
|---|---|---|
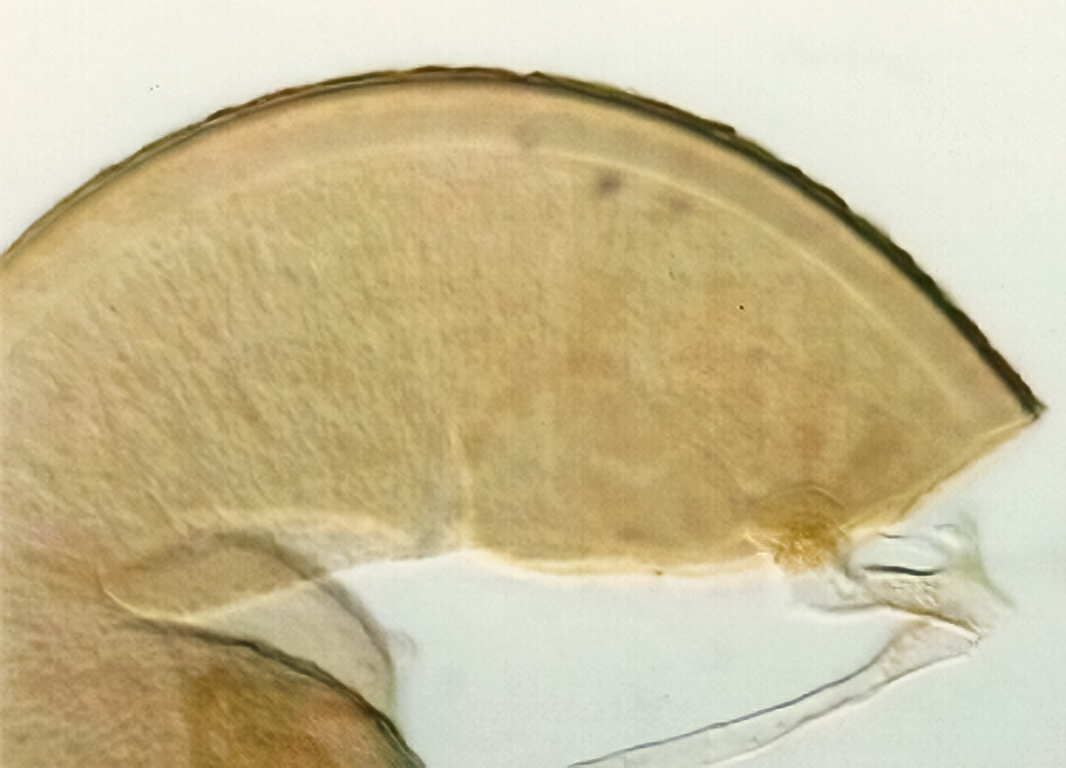 | 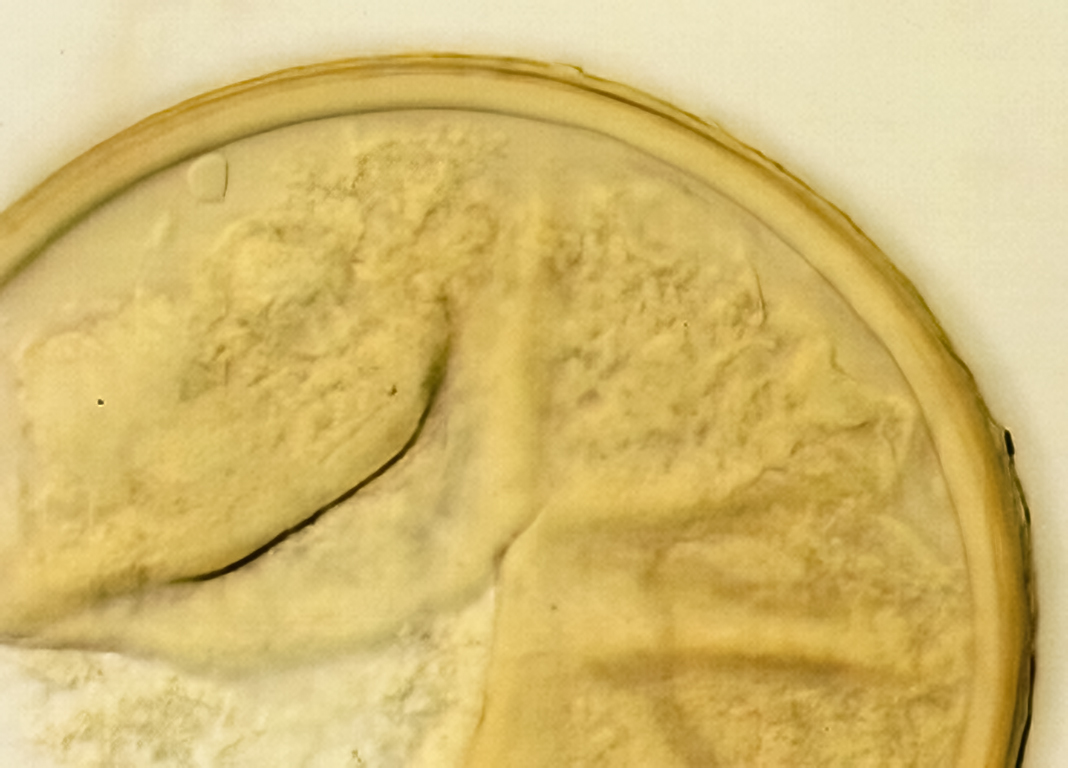 |  |
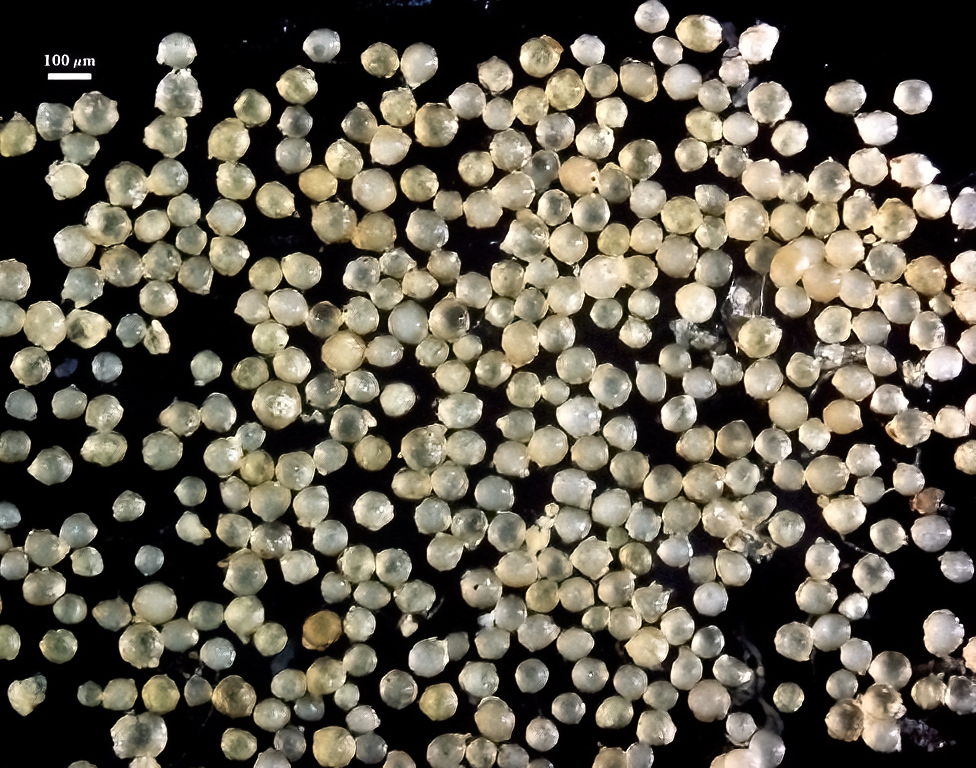
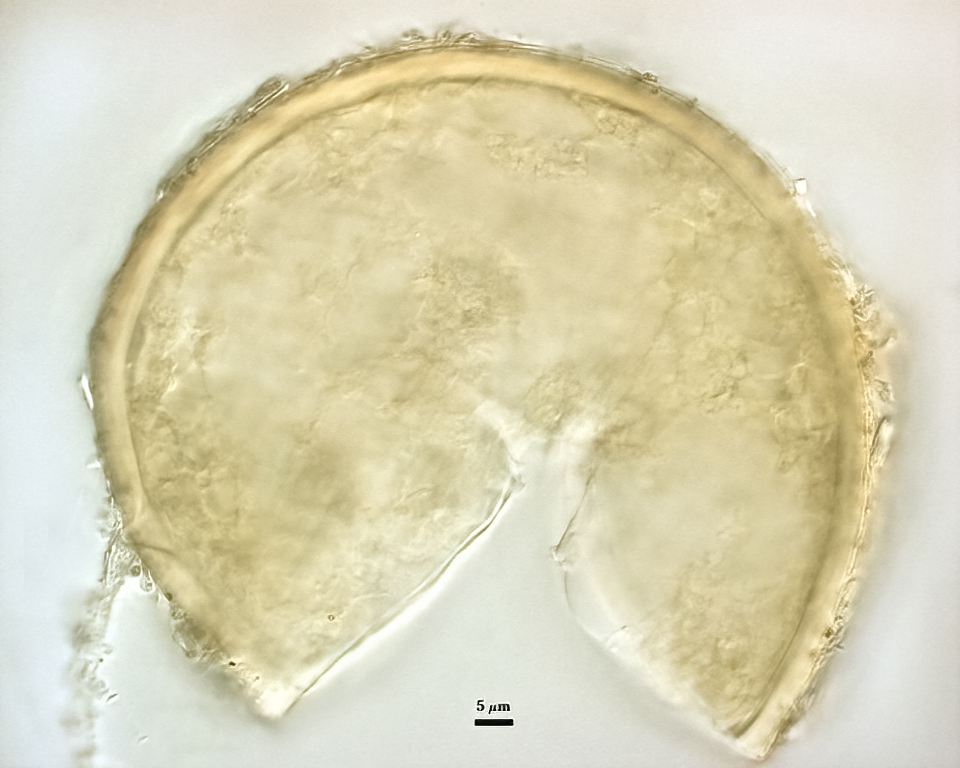
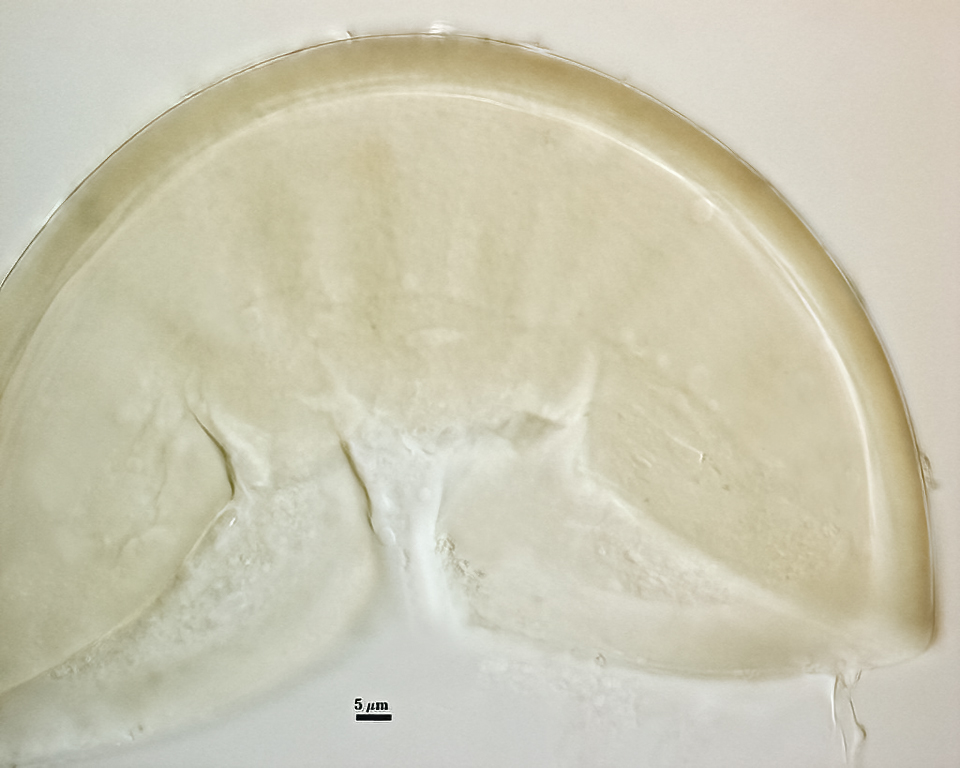
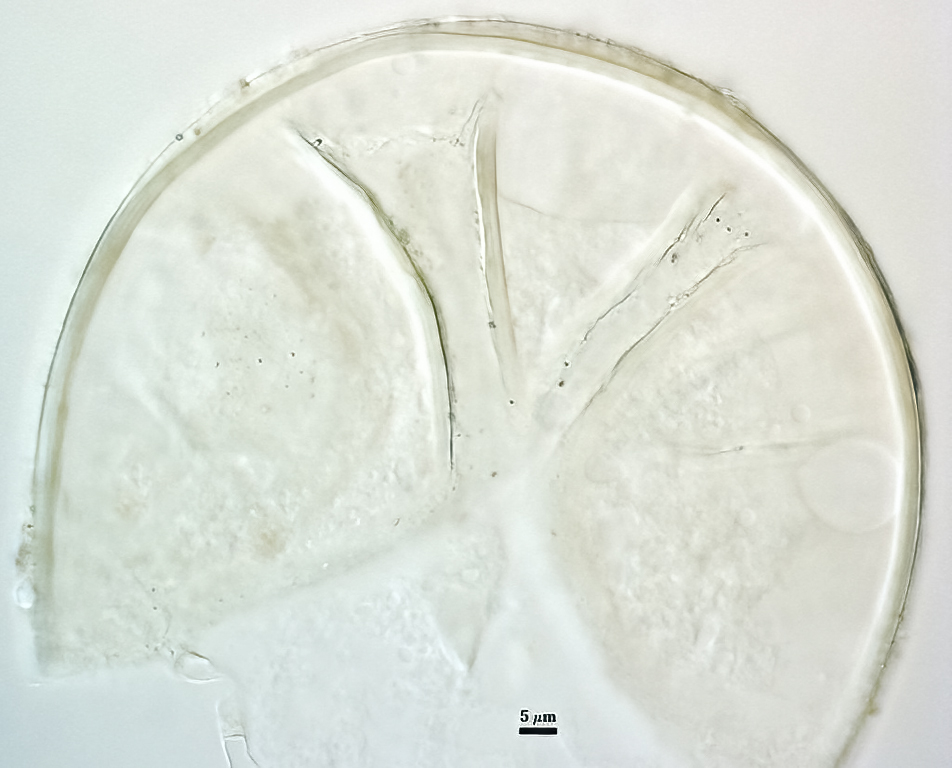
Spores formed singly in the soil; pale yellow to pale brownish-yellow; globose, subglobose, ellipsoid, pyriform, or irregular, often lenticular; (60-) 121 (-130) x (70-)118 (-200) µm.
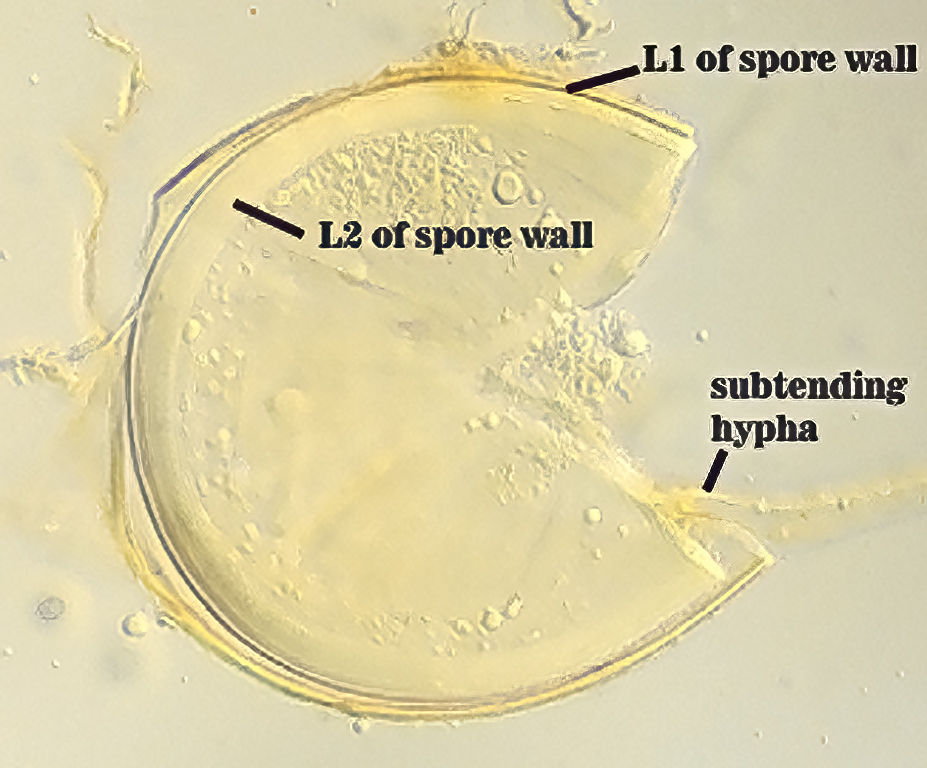
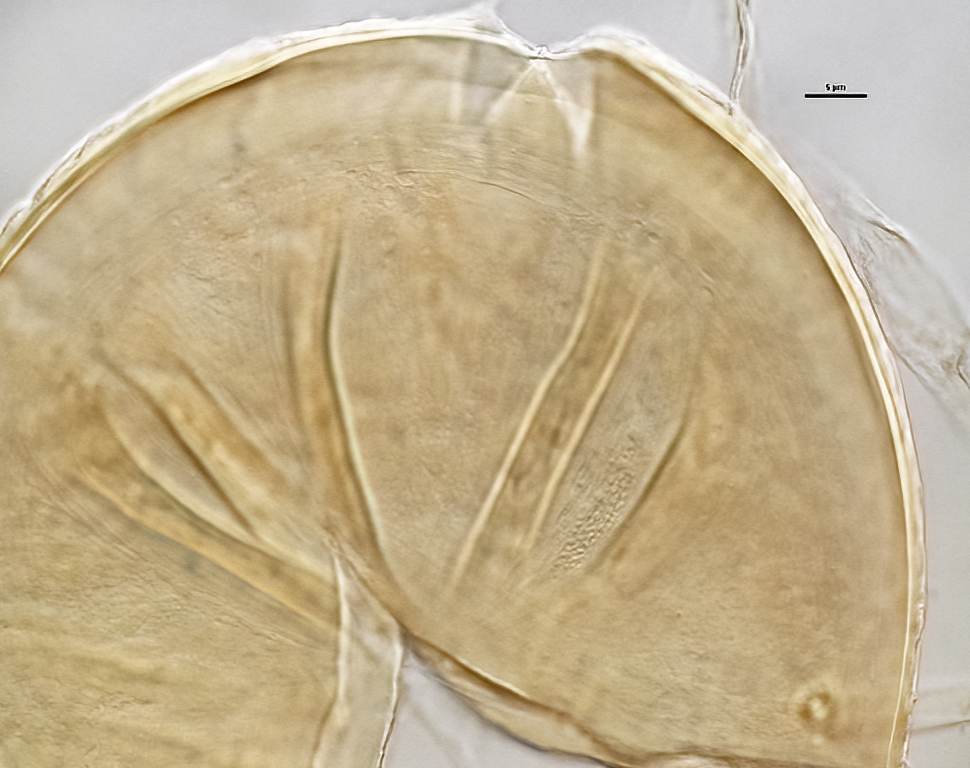
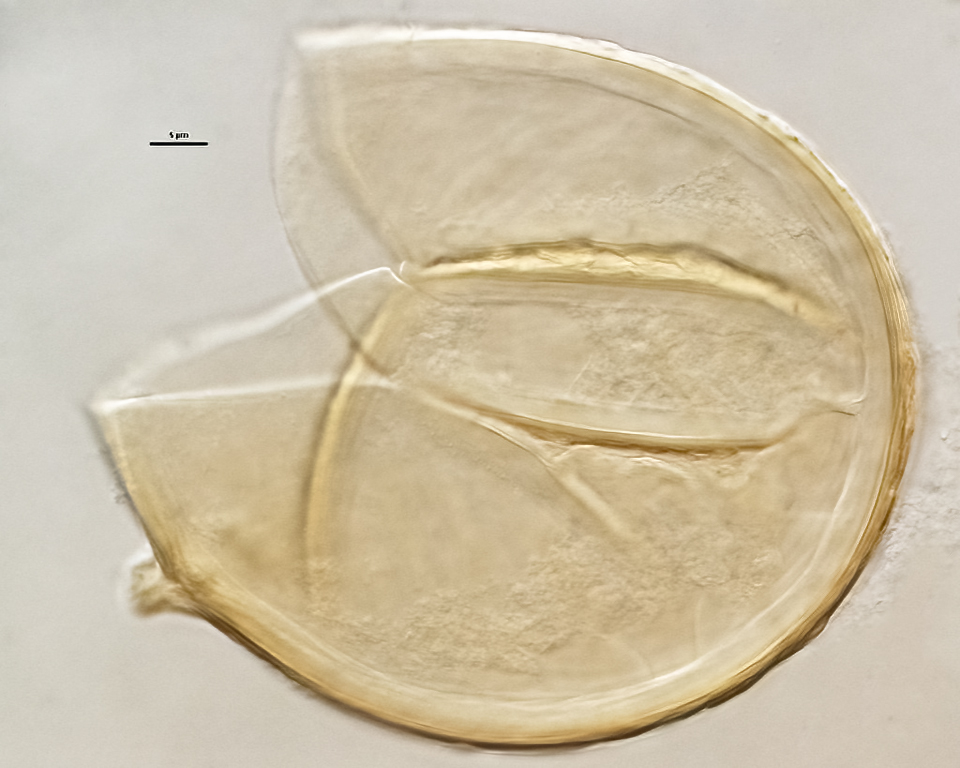
The spore wall consists of three layers (L1, L2, and L3). The outer layer (L1) is rigid, permanent, and consists of several sublayers (laminae), pale yellow to yellow-brown in color, 0.8-2.5 (-3.5) µm thick. This layer is described as fragmenting in some spores to leave irregular plates on the spore surface. The middle layer (L2) is pale yellow to brownish-yellow in color and 1-3 µm thick. The innermost layer (L3) has very fine sublayers (or laminae) that appear indistinct or fuse to take on a homogeneous look, hyaline to pale yellow in color (brownish-yellow in older spores), and 5-l l (-15) µm thick. One of the layers react in Melzer’s reagent.
The subtending hyphae usually is single, straight or slightly constricted at the point of attachment, hyaline to pale yellow in color, and 4.5-8.5 µm wide at the spore base. The hyphal wall consists of all three layers of the spore wall, although the innermost layer (L3) extends only 5-10 µm from the spore; 1-1.5(-2) µm in total thickness at the spore base and thinning to <1 µm thick 5-10 below spore base pore usually occluded by a granular plug.
The images below can be uploaded into your browser by clicking on the thumbnail or can be downloaded to your computer by clicking on the link below each image. Please do not use these images for other than personal use without expressed permission from INVAM.
High Resolution Images | |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Reference
- Koske, R. E. and W. L. Halvorson. 1989. Scutellospora arenicola and Glomus trimurales: Two new species in the Endogonaceae. Mycologia 81:927-933 .