Racocetra fulgida
(reference accession VA103B)
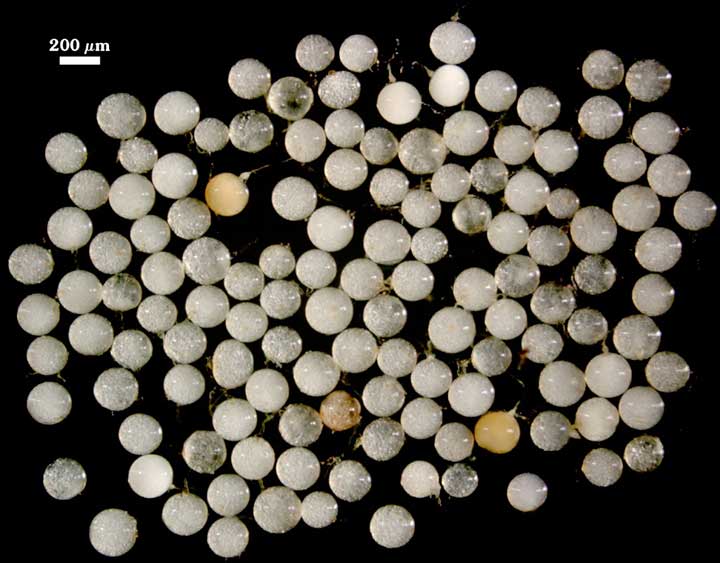
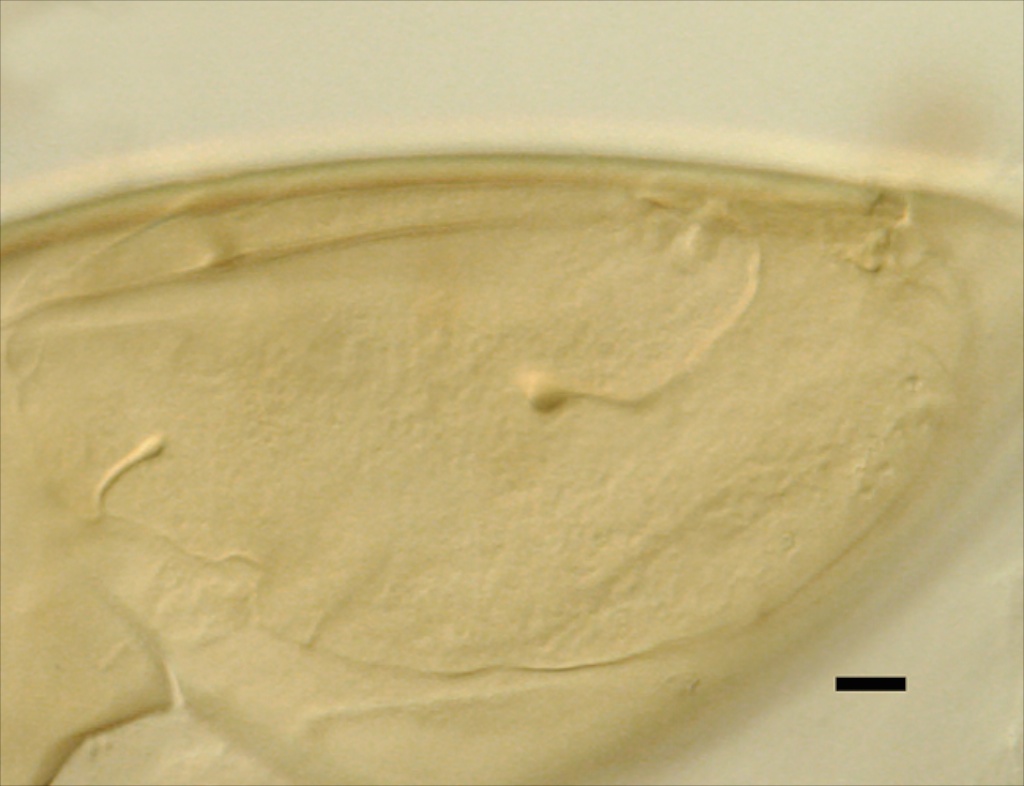
Whole Spores

 COLOR: Pale (0-0-5-0) to slightly darker cream color (0/0/40/0).
COLOR: Pale (0-0-5-0) to slightly darker cream color (0/0/40/0).
SHAPE: Globose, subglobose.
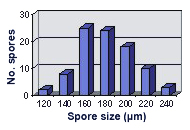
SIZE DISTRIBUTION: 120-240 µm, mean = 180 µm (n=90).
Subcellular Structure of Spores
SPORE WALL: Two layers (L1 and L2) that are adherent and of equal thickness in juvenile spores, with L2 thickening as the spore wall grows and differentiates further.
L1: Outer permanent rigid layer, smooth, off-white (0-0-5-0) to pale yellow (0/0/20/0), 0.7-1.8 µm thick
L2: A layer consisting of pale yellow (0/0/10/0 to 0/0/20/0), sublayers (or laminae) that increase in number with thickness, 4.5-6 µm thick (mean of 5.1 µm) in mature spores. This layer becomes bright yellow to gold color (0/0/100/0 to 0/10/100/0) in Melzer’s reagent.
| In PVLG | |
|---|---|
 |  |
| In PVLG and Melzer’s reagent (1:1 v/v) | |
|---|---|
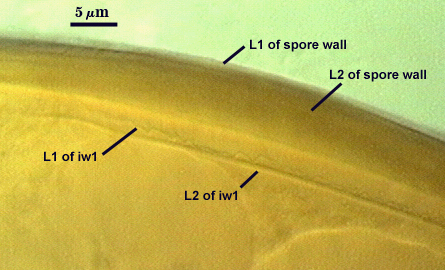 | 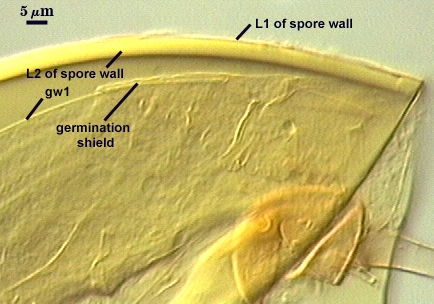 |
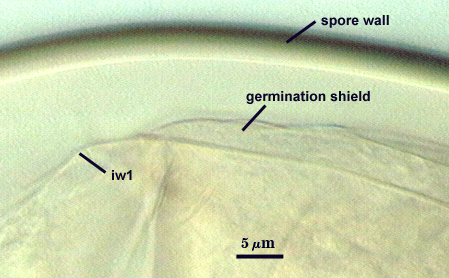
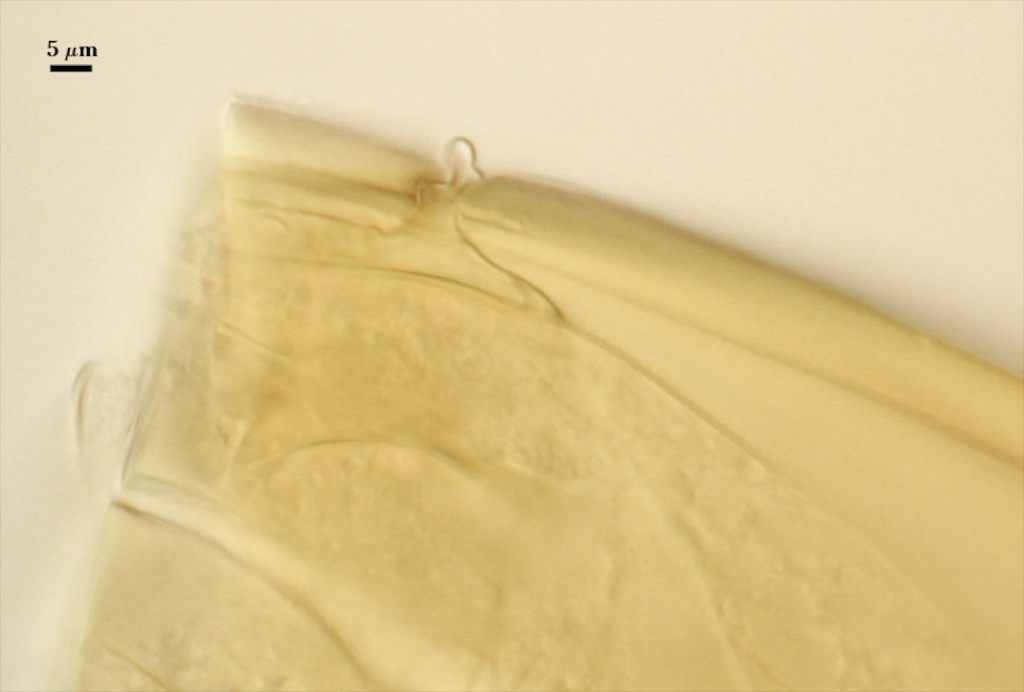
GERMINAL WALLS: One flexible inner wall (gw1) formed only after the spore wall and subtending hypha wall have completed differentiation; originates independently of the spore wall.
GW1: Two layers (L1 and L2) that in field-collected spores are so adherent that they appear as one layer (the condition of type specimens used to describe the species.) In spores from pot cultures, the outer layer often separates in small folds from parts of the wall giving the wall a blistered appearance. L1: A thin layer less than 0.5 µm thick and thus difficult to resolve without differential interference optics; no reaction in Melzer’s reagent. L2: A slightly thicker layer, 0.6-1.2 µm thick, with no reaction in Melzer’s reagent.
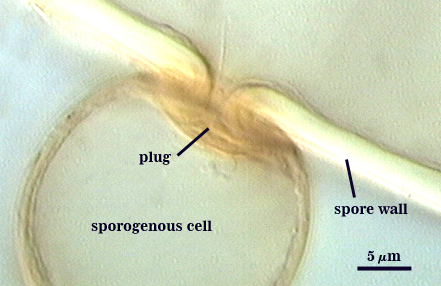
Subtending Hypha
WIDTH OF SPOROGENOUS CELL: 20-27 µm (mean = 23 µm).
SPOROGENOUS CELL WALL: Two hyaline layers (L1 and L2) probably are present (continuous with the two layers of the spore wall), but only L2 is readily discernible at the level of the compound microscope.
L2: Hyaline, 1.6-2.4 µm thick near the spore and then tinning to 1.2-1.4 µm beyond the sporogenous cell.
OCCLUSION: Closure by a plug concolorous with the laminate layer of the spore wall.
Germination
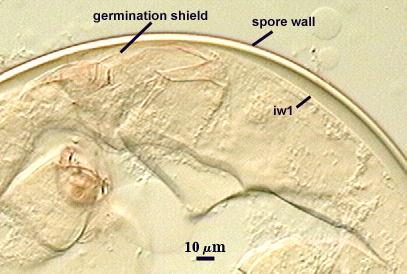
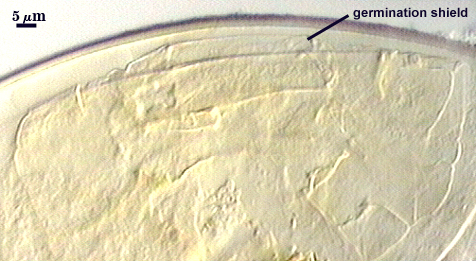
One or more germ tubes emerges from a germination shield. Shields usually have margins with only shallow convolutions; the surface smooth in many spores but papillate in others from a plan view.
COLOR: Hyaline or pale yellow (0-0-20-0).
SHAPE: Oblong, with length approximately 1.5 times width that of the width. Shield usually has margins with only shallow convolutions, the surface smooth in some spores (possibly immature?) but with a papillate surface in others. Position of the shield is on gw1.
| GERMINATION SHIELD | |
|---|---|
 | 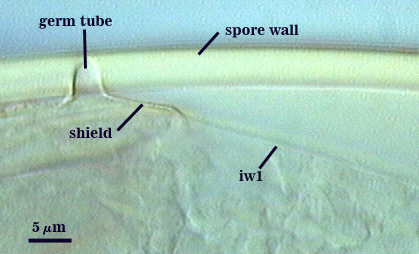 |
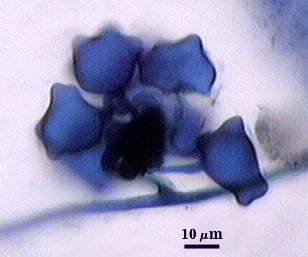
Auxiliary Cells
Cells in aggregates of 5-13 (mean = 8), subglobose, ovoid to clavate, borne on coiled hyaline hyphae, thin-walled (< 1 µm thick), pale yellow (0/0/10/0) in transmitted light; each cell with tuberculate surface, with swellings 1-5 µm high and 3-10 µm wide.
Extraradical hyphae of two morphological types: one wide (3-7 µm) and the other thinner (1.5-2.0 µm). The former usually is the infective hyphae at entry points and forms knobby swellings there are near auxiliary cells. Intraradical arbuscules and hyphae consitently stain darkly in roots treated with trypan blue. Arbuscular hyphae branch to from many fine tips from a swollen basal hypha. Intraradical hyphae 3-9 µm wide, with knobs, projections and swollen areas ( up to 12 µm wide), usually densely coiled near entry points and in outer cortical cells.
Mycorrhizae | ||
|---|---|---|
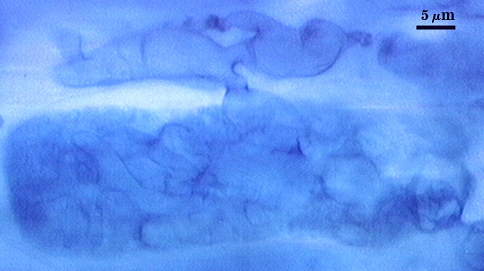 | 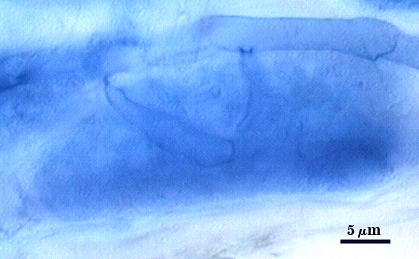 | 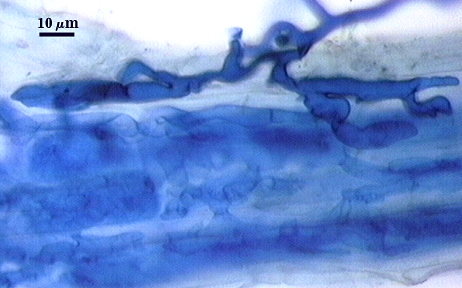 |
Notes
Immature spores are a tan color with slight rose tint (0/10/40/0 to 0/20/80/0). Resembles Gigaspora rosea under a dissecting microscope – spores need to be mounted on glass slides and broken to see the flexible inner wall and possibly a germination shield.
The images below can be uploaded into your browser by clicking on the thumbnail or can be downloaded to your computer by clicking on the link below each image. Please do not use these images for other than personal use without expressed permission from INVAM.
High Resolution Images | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |  | ||
 |  | ||