Glomus caledonius
(reference accession UK301)
| Immature Spores | Mature spores (with a few white immature) |
|---|---|
 |  |
Whole Spores
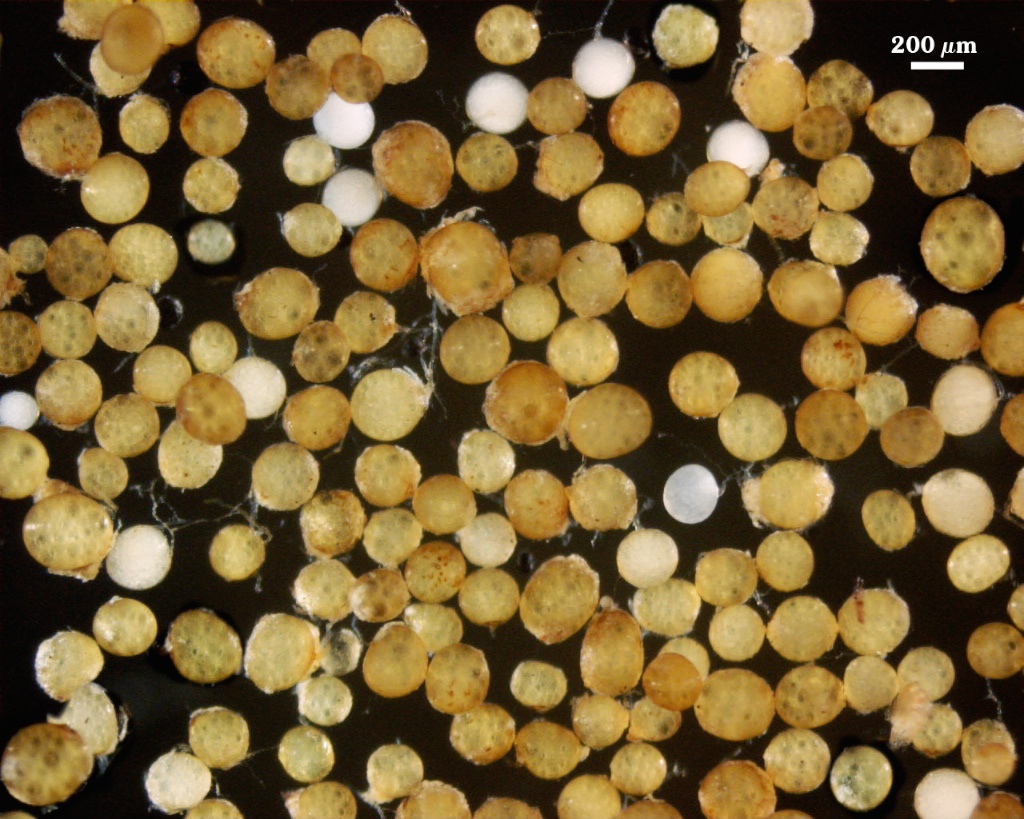
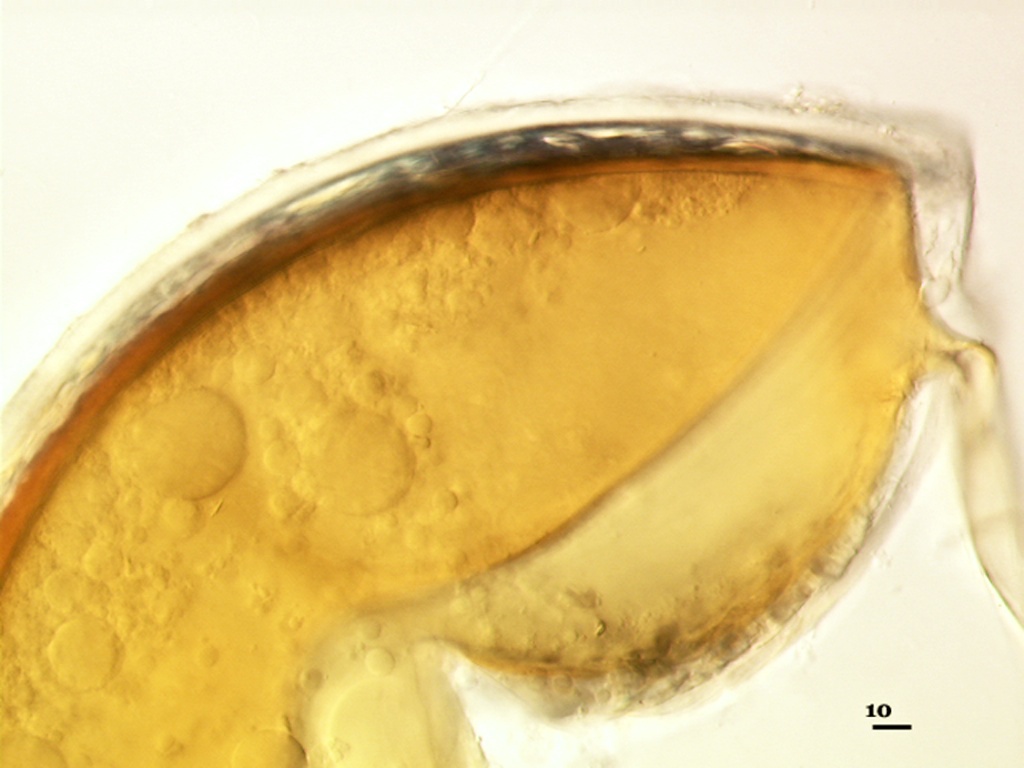
 COLOR: Pale orange-yellow (0-5-20-0) to yellow-brown (0-10-80-0); orange-brown (0-30-100-0) in the field or after long storage.
COLOR: Pale orange-yellow (0-5-20-0) to yellow-brown (0-10-80-0); orange-brown (0-30-100-0) in the field or after long storage.
SHAPE: Globose to subglobose, rarely irregular
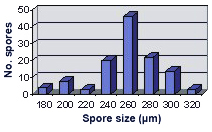
SIZE DISTRIBUTION:180-320 µm, mean = 259 µm (n = 120)
Subcellular Structure of Spores
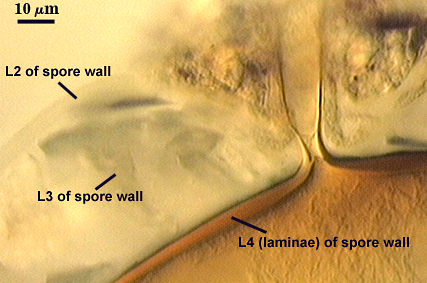
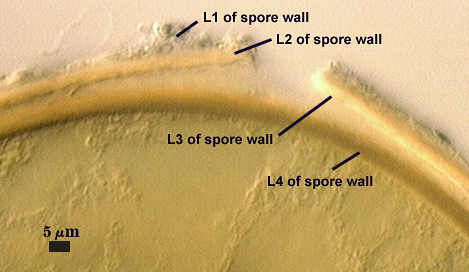
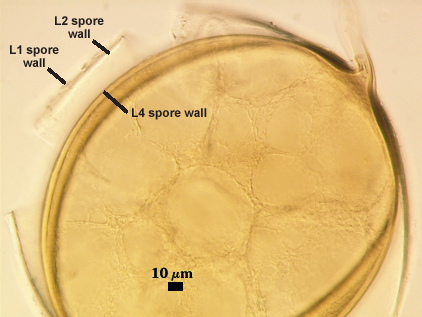
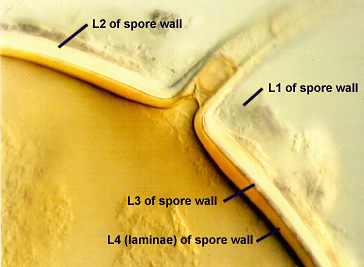
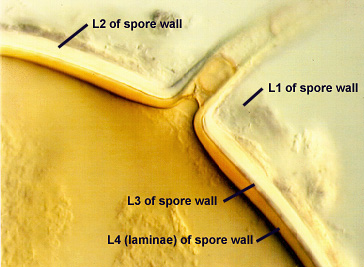
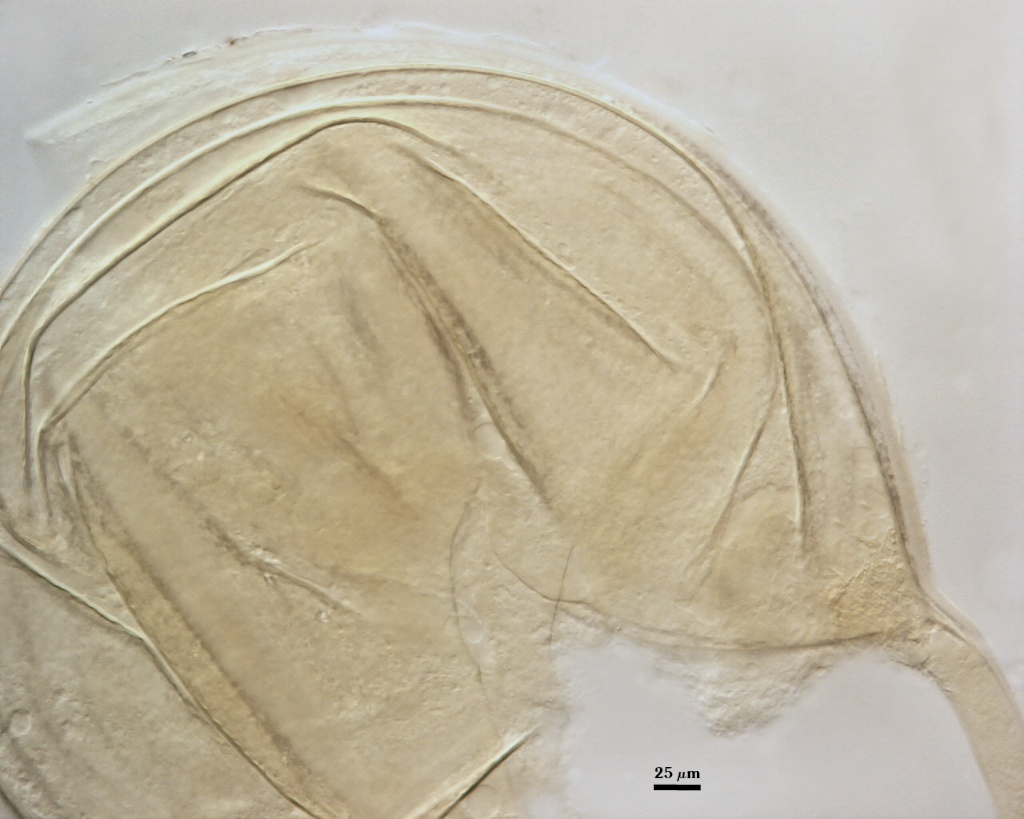
SPORE WALL: Four layers (L1, L2, L3 and L4) form successively during spore differentiation (see photos in sequence from left to right below). Only layers L1 and L2 are present in the most juvenile spores and also in their subtending hyphae. L3 is synthesized next, but it extends only a short distance into the subtending hypha and is therefore not an integral component of the hyphal wall. L4 forms last, and it appears simultaneously in subtending hypha and spore wall.
| Spore differentiation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
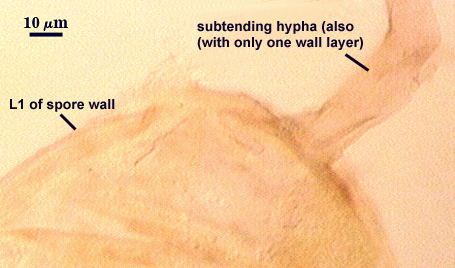 | 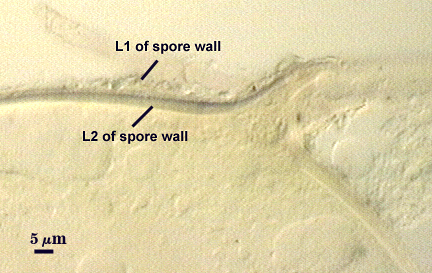 |  | 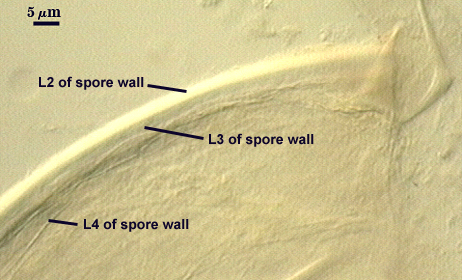 | 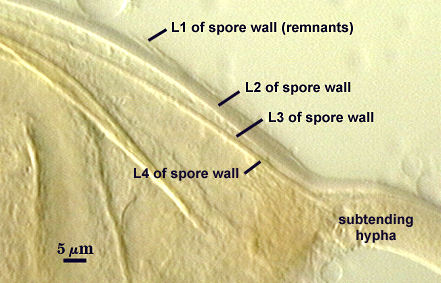 |
L1: Outer layer, hyaline, mucilagenous (pleiomorphic structure), 2-3.5 µm thick in juvenile spores, stains a pale pink (0-20-20-0) usually only on the wall of the subtending hypha near region of attachment to the spore.
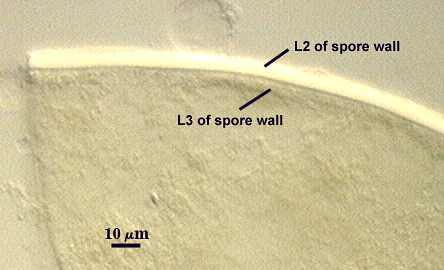
L2: A rigid hyaline layer, 1.5-3.5 µm thick in juvenile spores, no reaction produced in Melzer’s reagent.
L3: A hyaline layer of granular consistency, highly refractive in polarized light (differential contrast optics), usually attached to L2, 0.8-1.6 µm thick when L2 is not separated from L4, otherwise 2-3.5 µm thick.
L4: A layer consisting of pale yellow-brown (0-10-80-0) sublayers (or laminae) that originally is one very thin (< 0.5 µm) sublayer and then thickens with synthesis of additional sublayers; 4-6.4 µm thick in mature spores (mean = 5.2 µm).
| Holotype | Freshly extracted spores in PVLG | |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
| Freshly extracted spores in PVLG + Melzer’s reagent | ||
|---|---|---|
 |  | 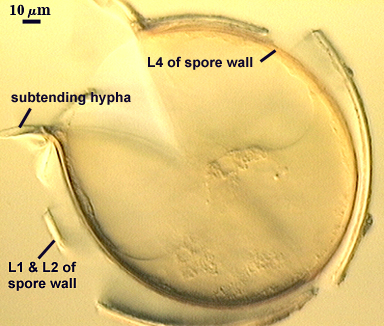 |
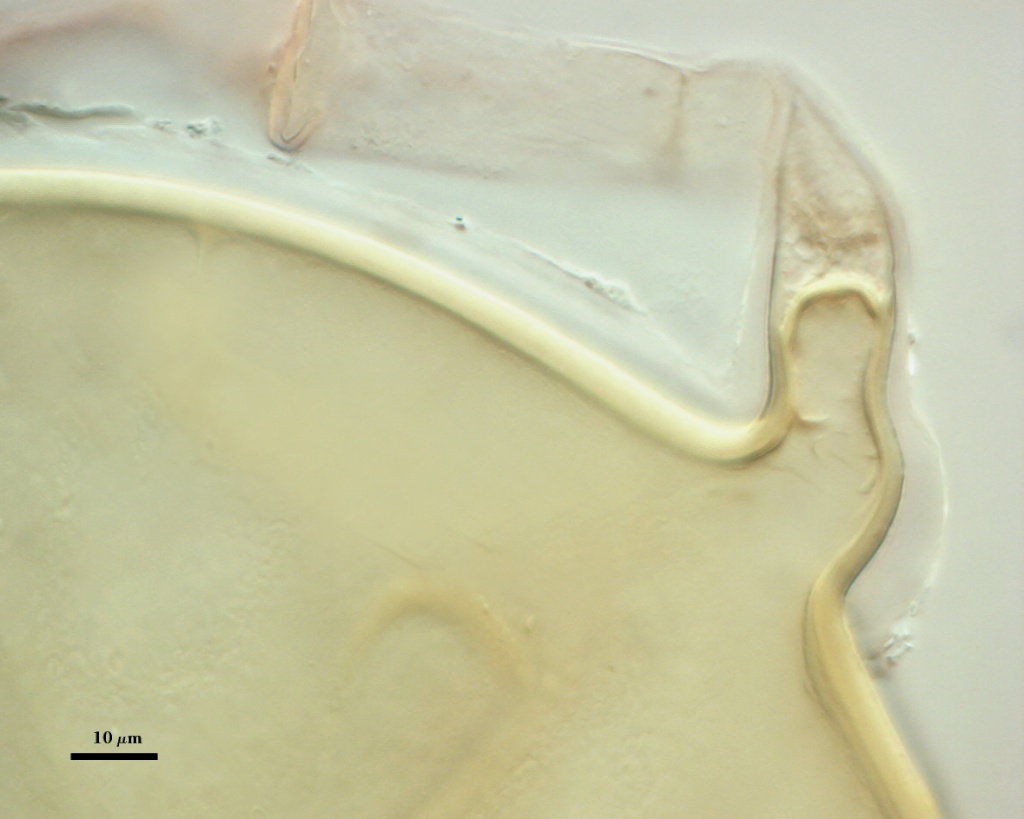
Subtending Hypha
SHAPE: Cylindrical, occasionally slightly constricted (see photos above).
WIDTH: 16-24 µm (mean = 18.2 µm)
COMPOSITE WALL THICKNESS: 4.4-6.0 µm
WALL STRUCTURE: Three layers (L1, L2 and L3) continuous with the same numbered layers in the spore wall. The outer layer (L1) is less than 1.0 µm thick in young spores, sloughing in older spores. L2 is hyaline layer; 1.8-2.9 µm thick near the region of attachment, thinning to less than one micrometer in hyphal wall > 50 µm from spore; sometimes degrading to varying degrees and then appearing as a thin granular layer (see last photo of developmental series above). L3 is a yellow-brown (0-10-60-0) layer, 2.5-3.2 µm thick near region of attachment, thinning to less than one micrometer in the hyphal wall > 50 µm from spore.
OCCLUSION: Innermost sublayer of the laminate layer of the spore wall (L4) bridges pore and resembles a recurved septum; positioned 8-32 µm from pore (see photos above).
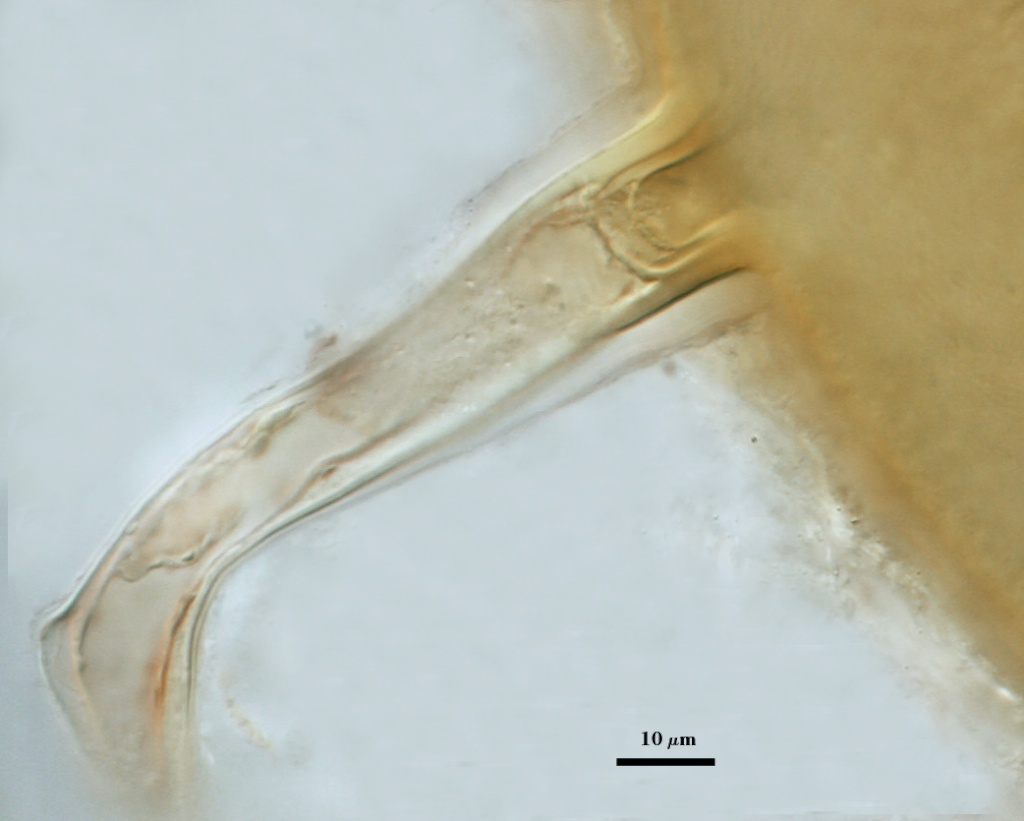
Germination
A germ tube emerges from the lumen of the subtending hypha, originating as regrowth of a hyphal septum. The germ tube can arise either at base of the spore (left photo) or further along the hypha (right photo).
| Regrowth of a hyphal septum | |
|---|---|
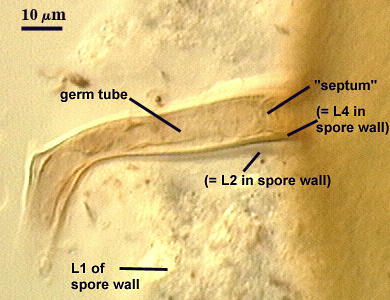 | 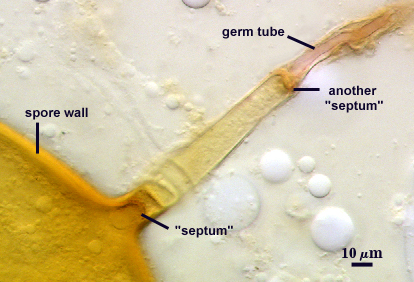 |
Mycorrhizae
Intraradical arbuscules and hyphae consistently stain darkly in roots treated with trypan blue. Arbuscules produce fine-branches from a swollen basal hypha(e) that are easiest to see as tips degrade. Intraradical hyphae 3-11 µm in diameter, with inflated areas up to 20 µm and knob-like projections distributed along length, usually densely coiled near entry points.
| Arbuscules in cortical cells of corn | ||
|---|---|---|
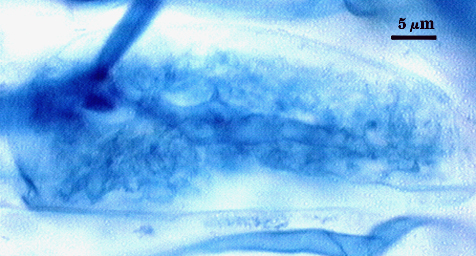 | 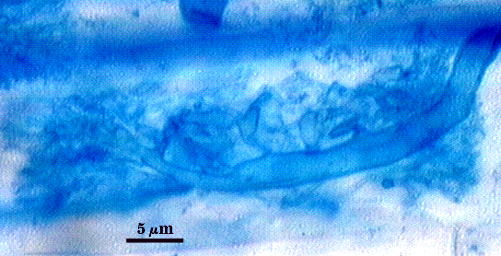 | 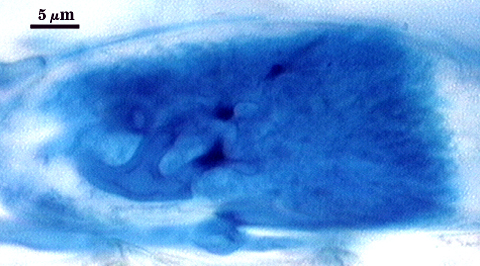 |
| Mycorrhizal structures in corn | |
|---|---|
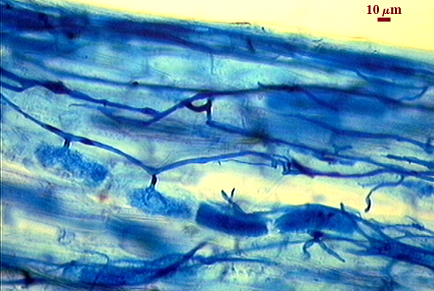 | 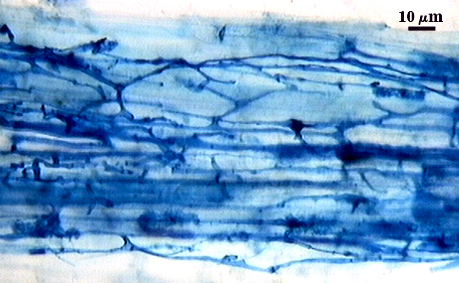 |
Notes
Under a dissecting microscope, spores of this species closely resemble Funneliformis mosseae. Published reports tend to confuse this species with both F. mosseae and R. clarus (which is of similar size and can be of similar color, but usually is more pale yellow to white).
The images below can be uploaded into your browser by clicking on the thumbnail or can be downloaded to your computer by clicking on the link below each image. Please do not use these images for other than personal use without expressed permission from INVAM.
High Resolution Images | |
|---|---|
 | 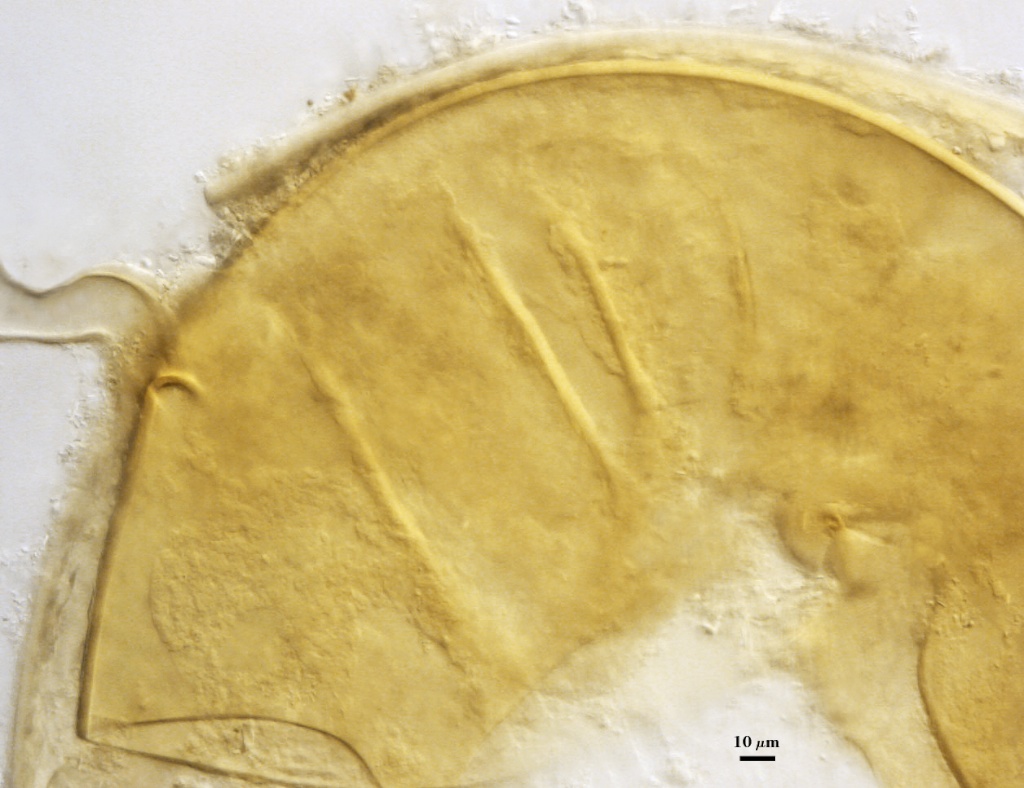 |
 |  |
 |  |